
Occupations: EMS Technicians
EMS Technicians
Overview of the profession:
Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Technicians, including Medical First Responders (MFRs), Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs), Advanced Emergency Medical Technicians (AEMTS) and Paramedics, play a critical role in the healthcare system by providing the first point of contact for individuals experiencing medical emergencies. Their training allows them to assess patients quickly, administer life-saving interventions, and stabilize patients for transport to healthcare facilities. EMS Technicians also serve as a vital link between patients and the broader healthcare system, helping with non-emergency transport to hospitals or other healthcare facilities. To become a licensed EMS Technician, individuals must complete a state-approved MFR, EMT, AEMT or Paramedic education program. Upon graduation, individuals must pass the corresponding National Registry Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) Exam and apply for licensure through the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS). Once licensed, EMS Technicians work at hospitals, fire departments, or private ambulatory services. The ability of EMS Technicians to work under pressure and make quick decisions can significantly influence patient outcomes, demonstrating their essential value in emergency healthcare.
MHC Insight collapsed four Emergency Medical Services (EMS) occupations into one EMS group for clarity of analysis surrounding the dental labor force. The EMS occupations included under the EMS grouping are Medical First Responders (MFR), Emergency Medical Technicians (EMT), Advanced Emergency Medical Technicians (AEMT), and Paramedics (EMT-P).
EMS Career Pathway
EMT Pathway
What is needed to become an Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Technician in Michigan?
To become an EMS Technician in Michigan, individuals can choose to complete one of two initial educational certifications: Medical First Responder or Emergency Medical Technician. To be eligible for certification through the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS), individuals must complete their education through a program approved by DHHS and pass the corresponding National Registry
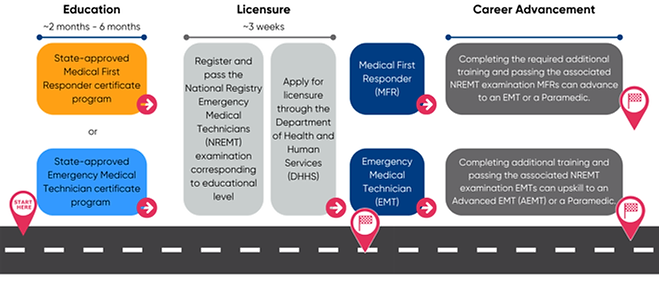
Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) Exam for their education level.
How can EMS Technicians advance their careers?
Yes, by completing additional education or training and passing the associated NREMT exam, MFRs can upskill into an EMT or Paramedic role, and EMTs are eligible to upskill to an Advanced Emergency Medical Technician (AEMT) or Paramedic role.
Paramedic Pathway

What is needed to become a Paramedic in Michigan?
To become a Paramedic in Michigan, individuals must first complete a state-approved Emergency Medical Technician (EMT) program and hold a valid or Specialist/ Advanced EMT license prior to being eligible to enroll in and complete an accredited paramedic program. To qualify for licensure as an EMT-Paramedic, individuals must pass the National Registry Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) Paramedic Certification Exam for their education level.
Why choose an EMT or Paramedic level of training?
Paramedics have a broader scope of practice within Michigan that allows them to perform more advanced medical procedures and administer a broader scope of medications. Due to their additional training, paramedics may also be eligible for higher wages than an EMT or Specialist/AEMT trained individual.
For current and comprehensive licensure requirements, please visit: www.michigan.gov/mdhhs/inside-mdhhs/legislationpolicy/ems
Current Workforce Data
We've provided the latest data from Lightcast below. Lightcast gathers and integrates economic, labor market, demographic, education, profile, and job posting data from dozens of government and private-sector sources, creating a comprehensive and current dataset that includes both published data and detailed estimates with full United States coverage.
Click on the images to enlarge them and review them in further detail.

2025 Hourly Wages
10th Percentile | 25th Percentile | Median | 75th Percentile | 90th Percentile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
$17.30 | $18.26 | $21.25 | $24.53 | $28.51 |
Top Posted Job Titles
-
Paramedics
-
Emergency Medical Technicians - Basic
-
Emergency Medical Technician Paramedics
-
Emergency Medical Technicians
-
Medical Equipment Delivery Drivers
-
Clinical Care Extenders
-
Paramedic Specialists
-
HBO Technicians
-
Field Paramedics
-
Flight Paramedics
Index Ranking
Paramedics EMTs
Paramedics ranked 10th, and EMTs ranked 27th (out of 36) "healthiest" profession according to the 2025 Michigan Healthcare Workforce Index.
Learn more here.
2025 Employment: 7,351
Projected 2035 Employment: 7,660 (+4%)
Highlighted Workforce Initiatives
Name: Allegan Area ESA CTE
Prosperity Region: 4
Description: Health-related CTE courses at Allegan Area ESA Tech Center include Health Care Science Foundations, Health Occupations Academy (where students can sit for the Patient Care Technician certification exam) and EMS. These courses have articulated college credit for eight different higher-ed institutions in Michigan.
Name: First Responder Apprenticeship Program
Prosperity Region: 7
Description: Lansing Community College has announced a new First Responder Apprenticeship program partnership between the college’s Health and Human Services Division (HHS), the Lansing Fire Department, and Capital Area Michigan Works! (CAMW). The apprenticeship program will address a critical shortage of emergency medical workers in the Capital region by providing existing firefighters with Emergency Medical Technician (EMT) training through Lansing Community College's EMT Academy, greatly increasing the services they can provide. The EMT Academy is offered to apprentices for free through a DOL Strengthening Community College grant and Workforce Development Institute funds.
Name: UP Workforce Innovation Network (WIN)
Prosperity Region: 1
Description: The U.P. WIN (Upper Peninsula Workforce Innovation Network) is a project funded by a grant from U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The purpose of the project is to increase Upper Peninsula residents' access to healthcare in the U.P. by expanding workforce training, education, and healthcare employment in the region. The plan is to focus on the development of community health workers (CHWs), community paramedics, and EMS professionals. Goals of U.P. WIN are to 1) expand the roles of paramedics and EMTs to assist in providing public health, primary health care and preventative services to underserved populations in the UP; 2) cross-train community health workers through NMU's Center for Rural Health and 3) enhance training for existing staff. (Note Dane: Maybe insert a piece about creating more sustainable and long-lasting health practices for rural communities in the UP)








